The patient was implanted for primary prevention of obstructive hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (resting gradient: 80 mmHg). He is asymptomatic, but note the sudden death of two of his brothers, one of whom also had OHCM, with ventricular tachycardia bursts, a genetic mutation, and significant septal fibrosis at MRI. The defibrillator is dualchamber given that the patient is bradycardic under beta-blocker therapy, and in the hope that the DDD pacing from the RV with complete RV capture while maintaining atrial systole will decrease the obstruction in the long term. A follow-up control was conducted on day 1, and deemed satisfactory.
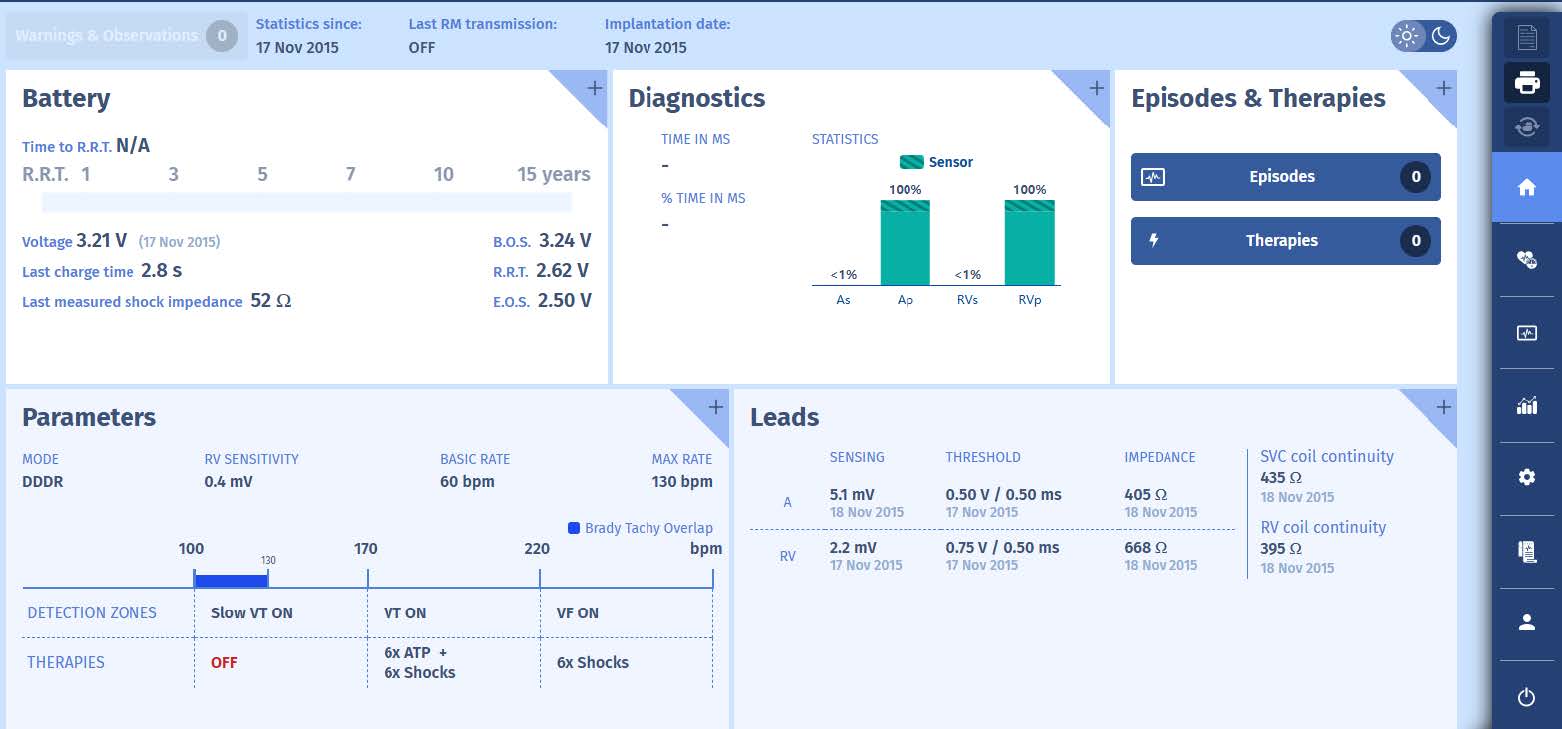
However, two weeks later, a telemedicine alert was transmitted.
This is when the patient comes into clinic after the alert
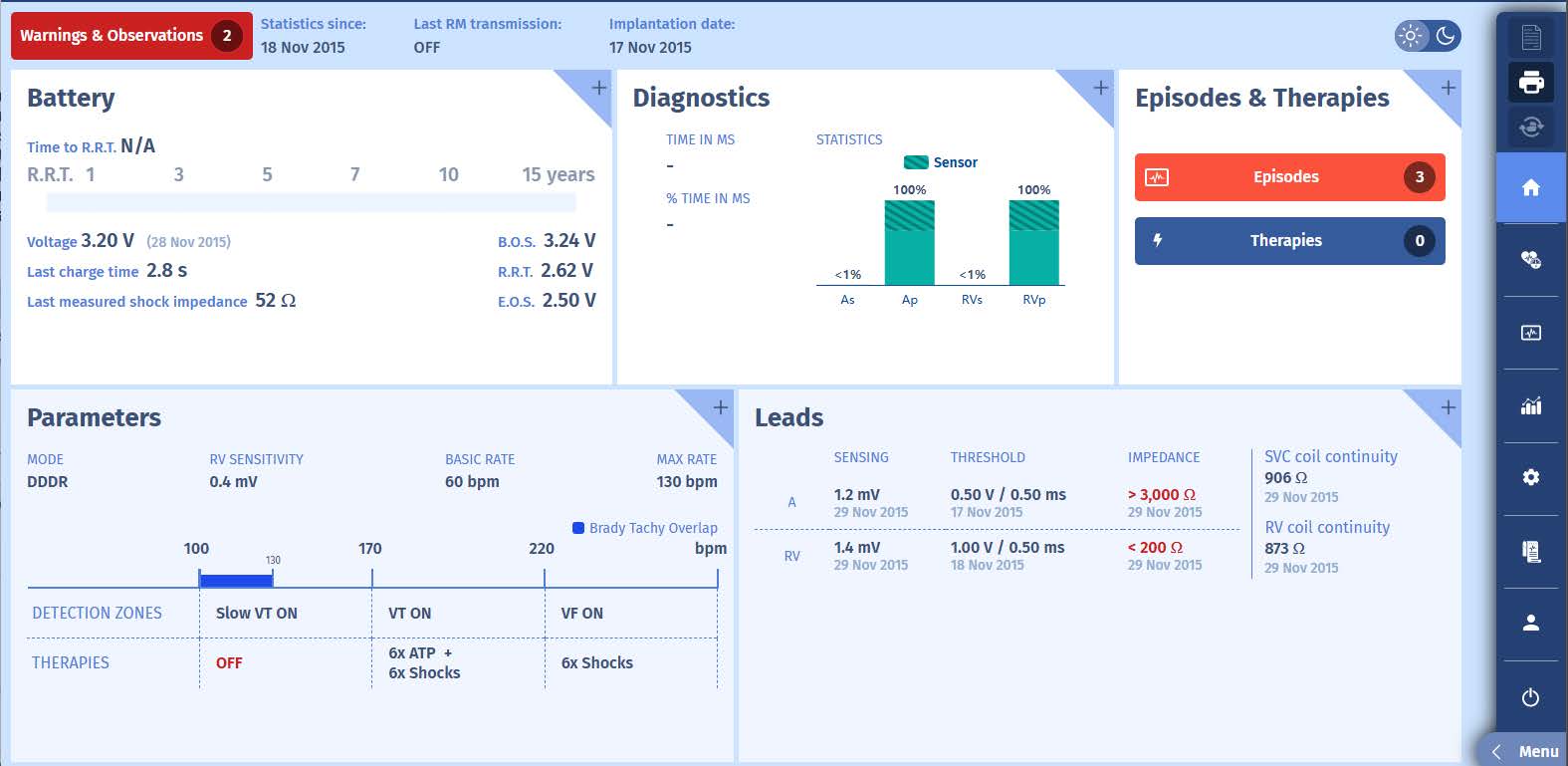
Additional information from the alert screen
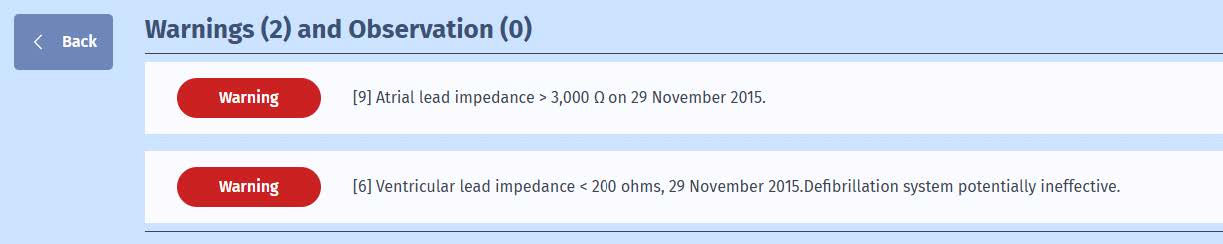
Lead sensing and impedance trends
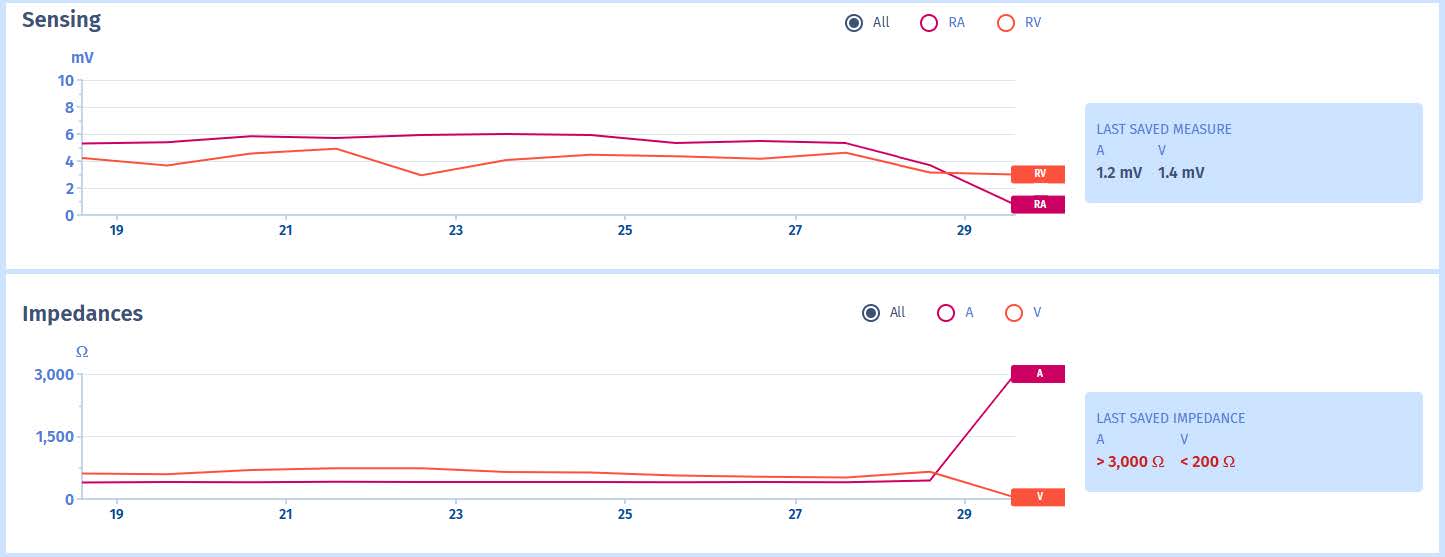
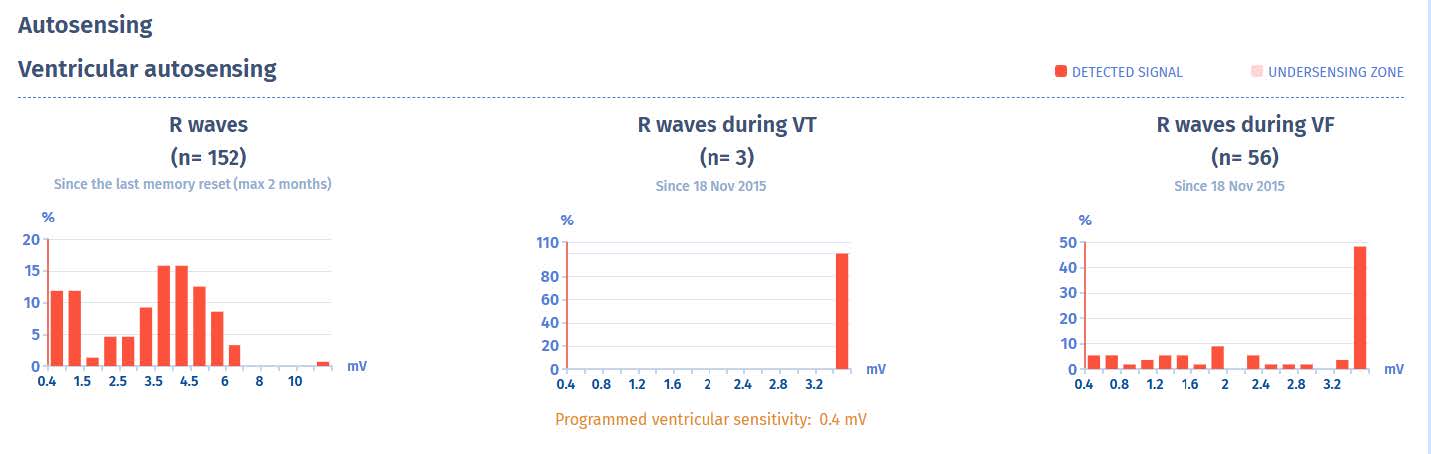
Ventricular signal amplitudes
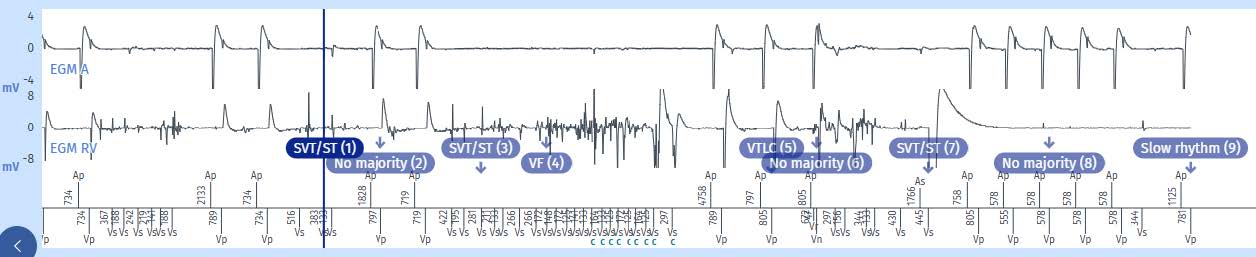
EGM saved into the memory of the device as «VF»
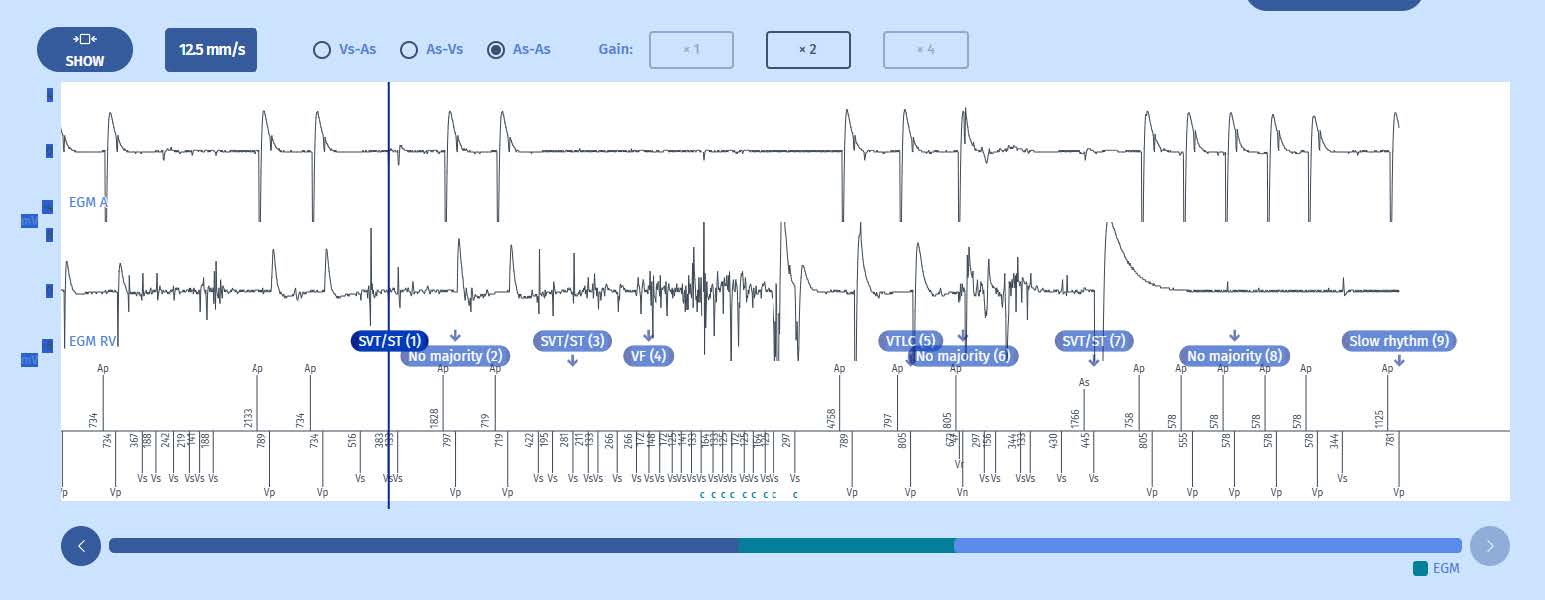
Episode recorded during the emergency follow-up, after manipulation of the defibrillator case through the skin
Interpretation
- At the first follow-up control, 24 hours after defibrillator placement, ventricular sensing is low at 2.2 mV. This parameter must be re-assessed after a few days, although if the detection
value remains very low or decreases again, it will be necessary to discuss the repositioning of the ventricular lead. A minimum value of 5 mV is allowed for the amplitude of the R wave
at the time of lead placement.
- The teletransmission initiated an alert due to abnormalities in measured lead impedances. The atrial impedance exceeded the upper limit of 3000 Ohm, signalling a fractured conductor,
and the ventricular lead exceeded the lower limit of 200 Ohm, signalling an internal insulation fracture.
- These anomalies occurred at the same time on both leads and suggest a mechanical aggression on the two leads, probably related to a traumatic lead fixation given their
occurrence soon after the installation of the device.
- The problem cannot be a connection fault at the level of the defibrillator case, since in this instance, the impedances of the two leads would be beyond the maximum values.
- Only 152 R-waves were sensed since the defibrillator is constantly pacing. R-waves in VF and VT are fracture artifacts and can have a very large amplitude.
- These artifacts occurring in runs lead to false VF diagnoses, which induces capacitor charges.
- It is necessary to reoperate urgently and change the two leads. In the meantime, the therapies are inactivated.
- The handling of the material through the skin « finished off » the leads. The last electrogram no longer reveals any physiological signal, and the artifacts saturate the atrial channel.






