Levels of aggressiveness
Patient
A 56-year-old ischemic patient, with ejection fraction of 30% and symptoms of heart failure, implanted with a dual chamber ICD, comes for a check-up.
Programming

EGM
Interval plot
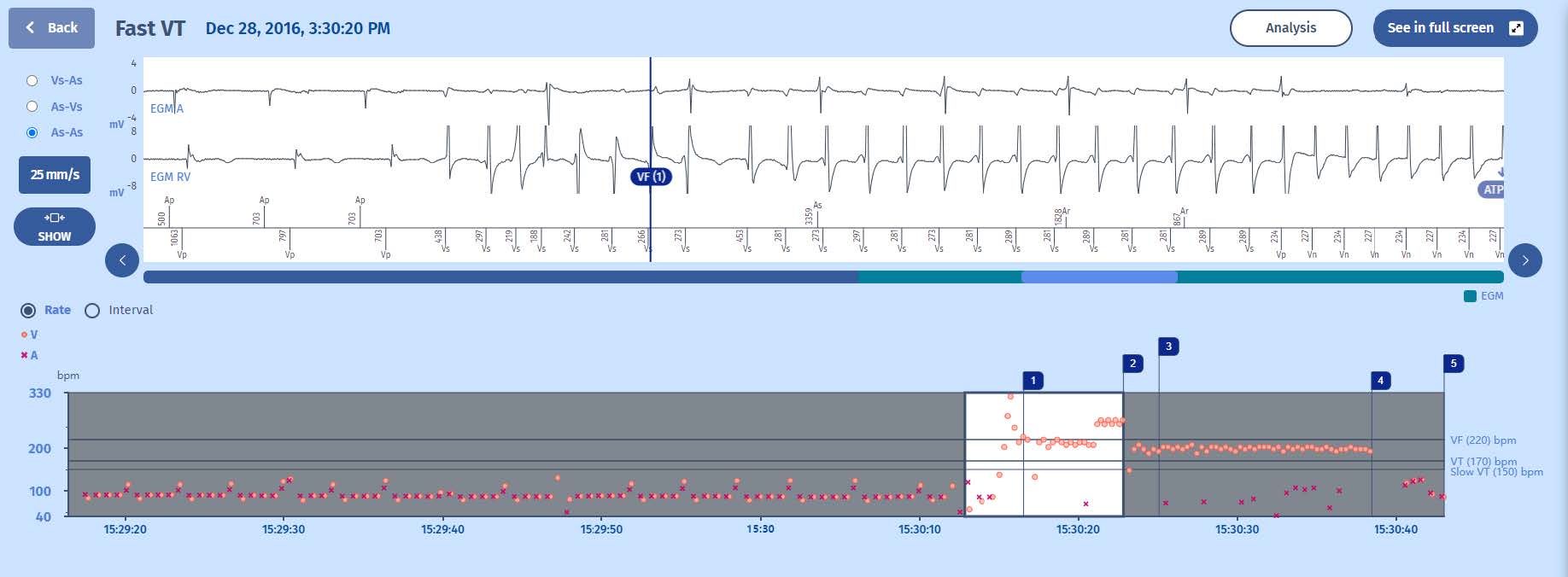
1 The onset of a tachycardia at the boundary of the VT and VF zones.
2 That the established diagnosis is VF
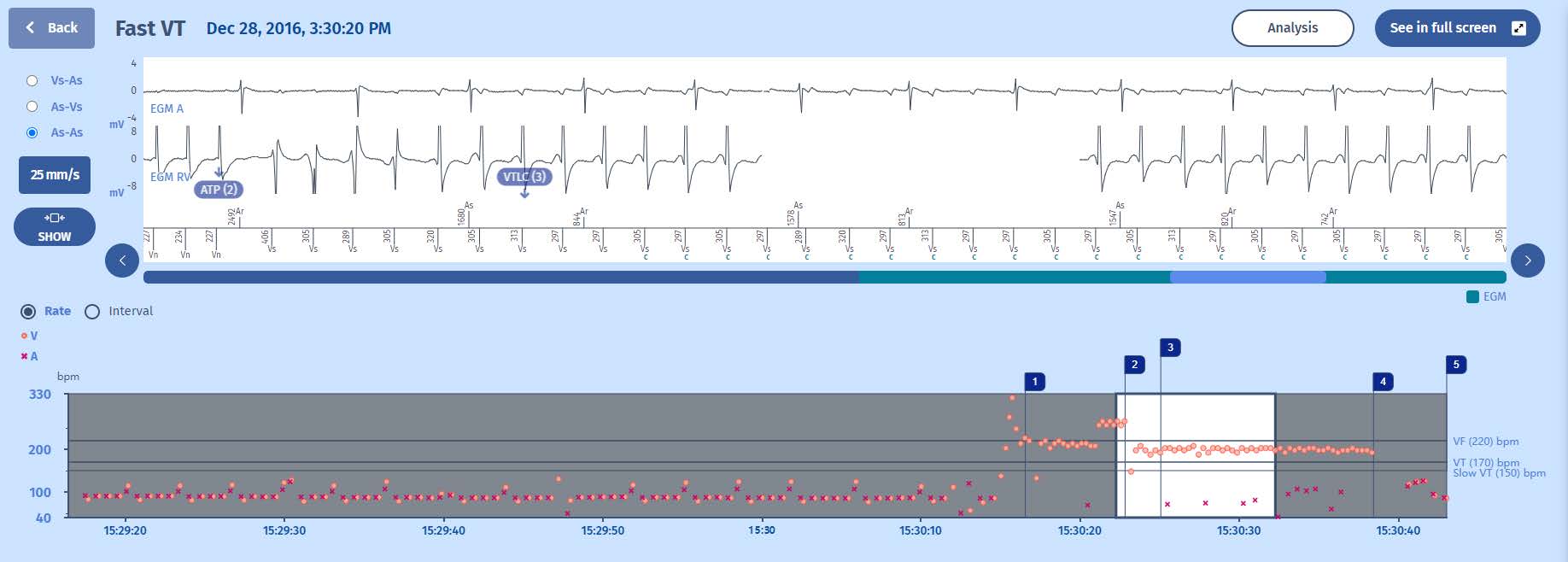
3 That an ATP burst is delivered which slows down the tachycardia and enters the latter into the VT zone
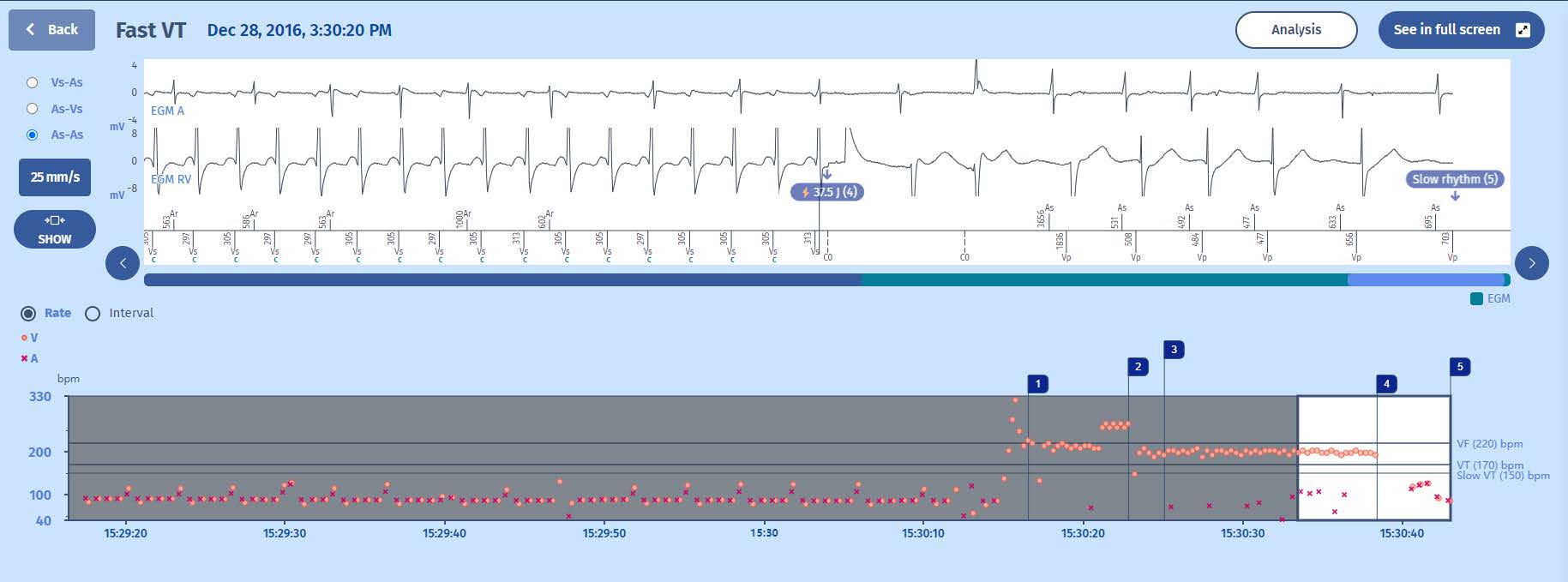
4 However it is a 42J shock that is called upon and not the ATP sequences programmed in this zone
5 With return to slow rhythm
Explications
During the course of the electrically-driven atrioventricular rhythm, a ventricular tachycardia begins, detected in the VF zone (VF marker (1)).
- A persistence of 16 cycles is applied, and the diagnosis is not modified even if one of the cycles is of 453 ms, since this does not change the majority (at each cycle, at least 6 out of the 8 preceding cycles are in the VF zone) .
- At the end of this persistence, and because each of the last 4 cycles is in the Fast VT section of the VF zone and the rhythm is stable, the ATP sequence programmed in the Fast VT zone is triggered.
- During the redetection phase which follows the ATP, the first 4 cycles have a different morphology compared to the cycles preceding the ATP, suggesting the influence of this sequence on the tachycardia circuit, without however terminating it. Thereafter, the tachycardia is of the same morphology although a little slower, diagnosed as VT after 6 cycles in the VT zone.
- During the VF persistence, the VT counter has also increased. However, it nevertheless takes 4 additional cycles for the VT persistence counter to be fulfilled (since the number of VT persistence cycles is programmed to 20 cycles).
- It is a shock that is applied, the first of the VT zone.
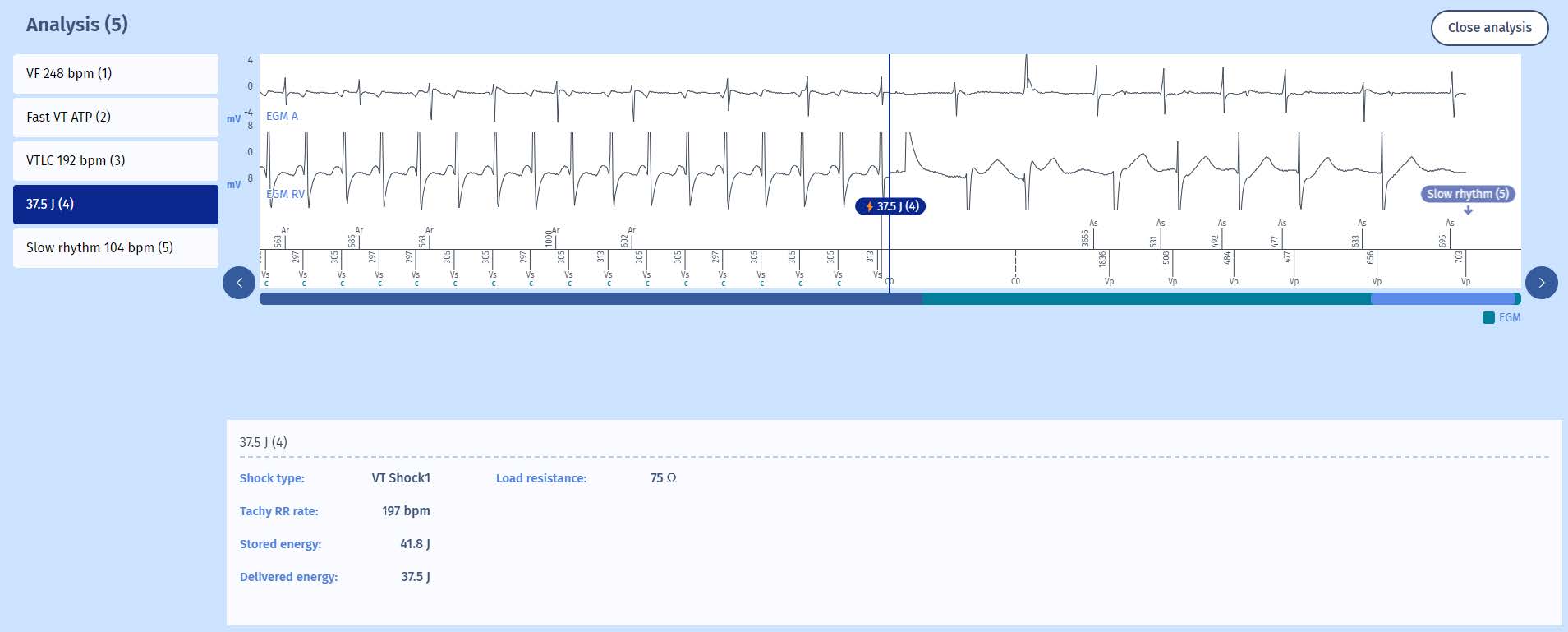
- Indeed, the burst of the Fast VT zone has completed the first series of therapies for all of the zones. It is therefore the second line of therapy which is called upon, and thus a VT Shock 1 is delivered as confirmed by the analysis corresponding to this shock in
the EGM. The measured impedance is 75 Ohm.
Comments
- This episode occurs in a context of a nocturnal rhythmic storm since several ventricular tachycardias occurred in less than 24 hours, terminated by Fast VT ATPs. These resulted in palpitation symptoms and telemedicine alerts. The patient recalls a high
consumption of alcoholic beverages during Christmas Eve… It should be remembered that the rhythmic risk is greatest in the 36 hours following the ingestion of alcohol, and which corresponds to the total elimination time of acetaldehyde, a breakdown
product of ethanol by the liver, an agent known to damage cell membranes.
- All of the ATPs were effective at the first attempt on each episode, thus avoiding the occurrence of shocks which would have made the patient present earlier. Analysis of the transmissions the next morning, leads to convening the patient to come to
the hospital. Unfortunately, the patient had an episode on route which resulted in a shock. However, we can surmise by this example the importance of having a remote transmission function that gave the alert and certainly avoided the patient from
experiencing other additional shocks.
- The prognosis for patients who have had a rhythmic storm is very poor, and more than 50% of these patients will have died after one year of follow-up. These statistics are however those which preceded the era of ablation. This patient underwent a
ventricular radiofrequency ablation session and to date has not had any recurrences while concomitantly refraining from the use of alcohol.
Take home message
When a line of therapies is exhausted in a given zone, and that the ventricular tachycardia changes zone, it is the following line of therapies which is called upon in the new zone with an aggressiveness level always higher or equal to the previous level, and so forth. There is therefore a progressive escalation of the therapies without any fall-back as long as the event remains in the same episode.
This is the reason why we can immediately observe shocks in the new zone since an ATP in the Fast VT zone had already been delivered. In the present example, the Fast VT ATP burst was immediately applied. With the tachycardia slowing down into the VT zone, it is the first shock of the VT zone which is called upon, as the ATP therapies are concluded (albeit in the VT zone).




