68-year old patient has been implanted with an ICD in the context of primary prevention for ischemic cardiomyopathy. A telemedicine transmission led us to call the patient for an emergency consultation, the latter having experienced a syncope and received a shock.
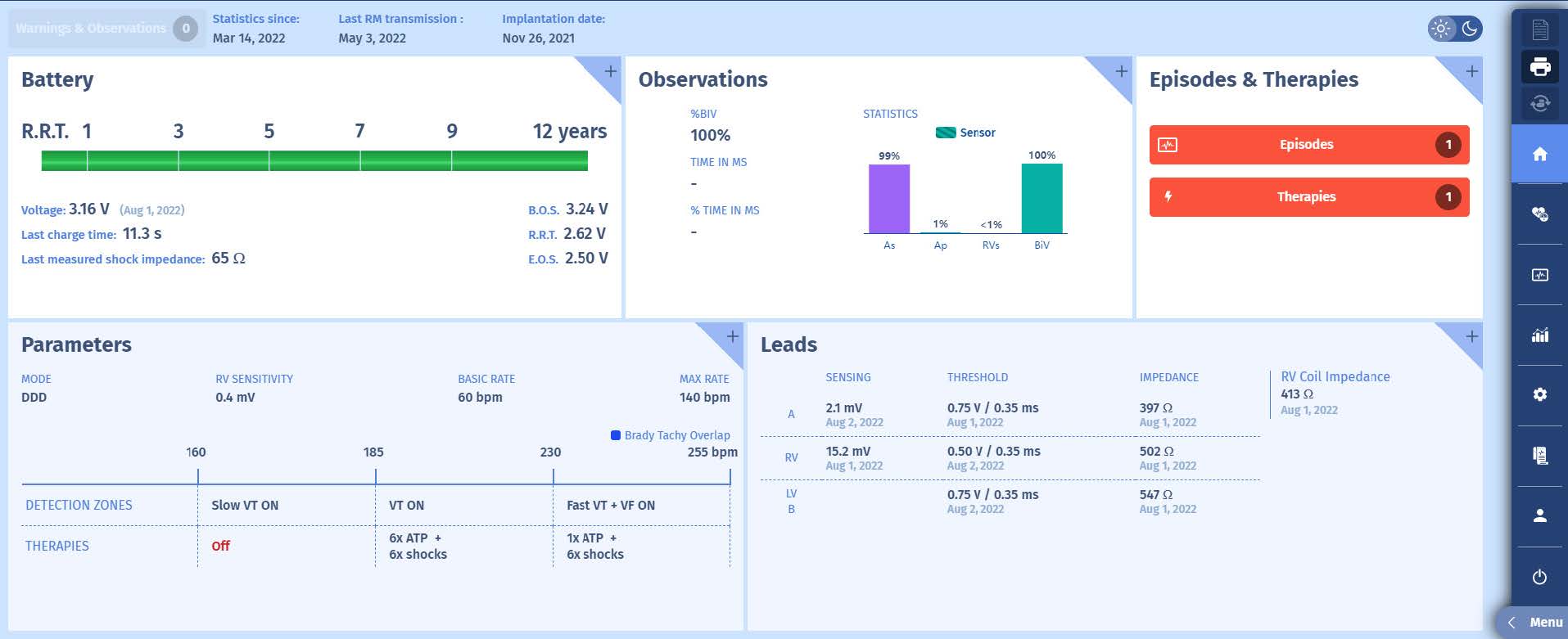
Here is the overview screen, notice that there has been one episode with therapies;

The following three screens show the episode:
This clinical case illustrates the basis of the functioning of a defibrillator and its intended purpose: the termination of a fatal ventricular rhythm disorder by a shock. In the summary screen, we can see that the leads are working perfectly, and that the device
battery is new with an output voltage of 3.16 V. Programming is consistent with current recommendations. Three zones are programmed: a Slow VT monitoring zone, without treatment; a VT zone with bursts, ramps and maximum shocks; and a
VF zone with a FVT section up to 255/min, with a burst if the FVT is stable, followed by max shocks, and a pure VF section with maximum shocks. Based on the stored memory, the device reports no mode switches, and there is 1 episode with
treatment . The last shock provided an impedance value of 65 Ohm.
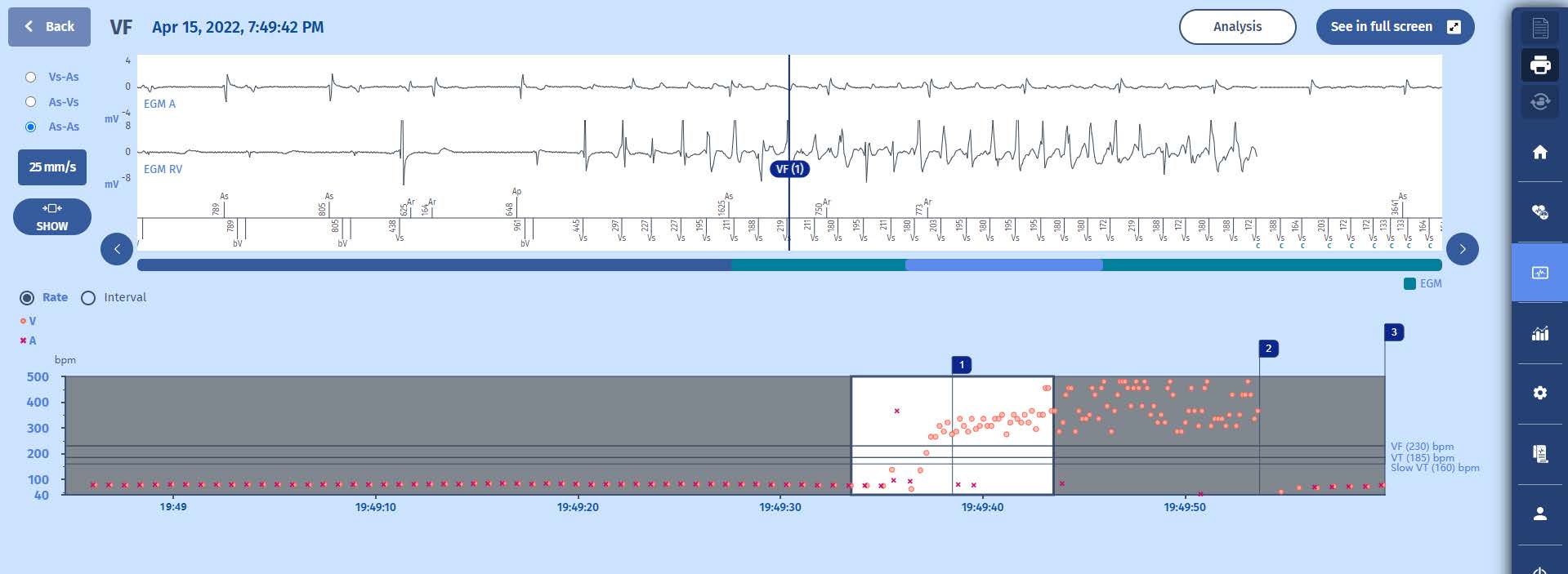
Tachogramme
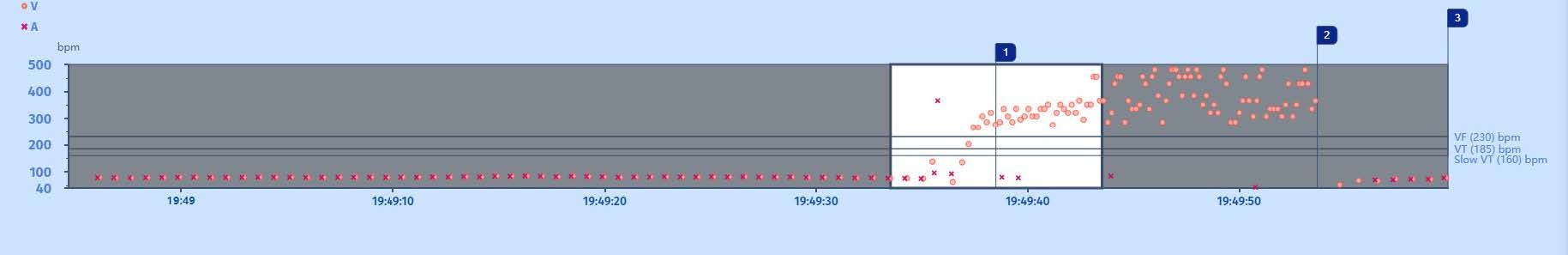
Onset of a very fast tachycardia in the VF zone with high cycle variability, for which a quick diagnosis of VF is made with delivery of a shock restoring the slow rhythm.
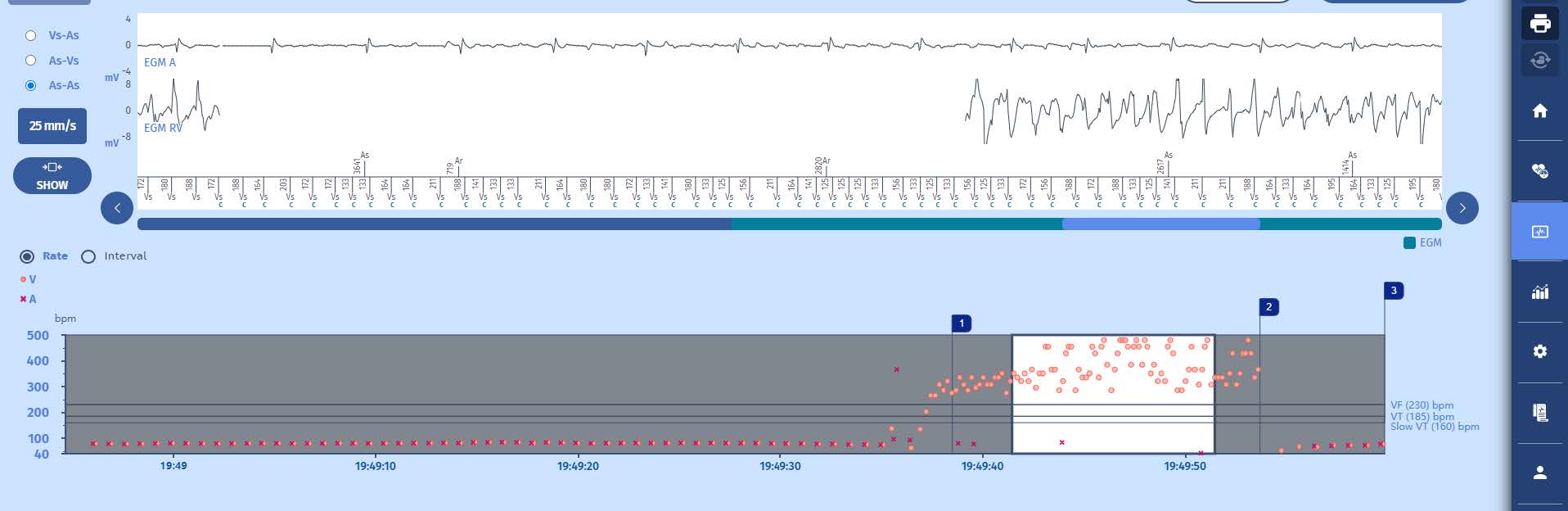
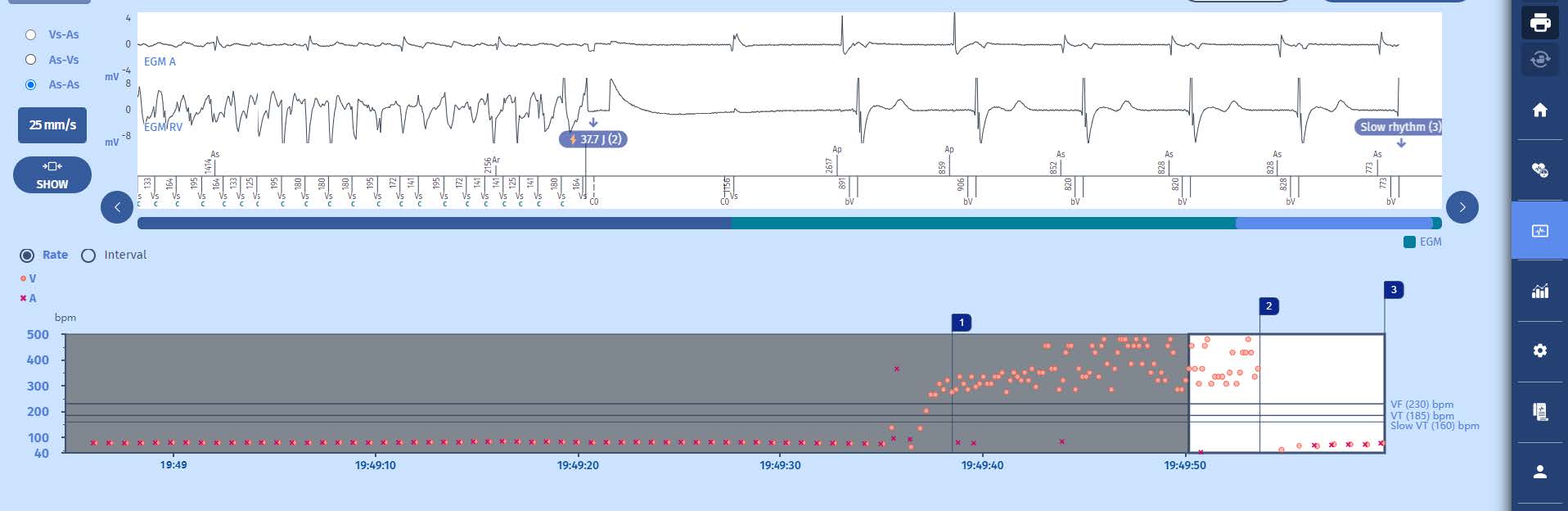
EGM
1 The tracing confirms the onset of a very fast ventricular fibrillation (VF (1)) detected above 255/min at nearly 300/min, and triggering a charging of the capacitors (C markers) after a persistence of 20 cycles. The VF episode is perfectly detected.
2 Throughout the charge, the VF majority is analysed cycle-by-cycle and the charge continues as long as the VF majority does not change to SVT/ST or SR (Slow Rhythm).
3 Upon completion of the charge of the capacitors at 42 J, the shock (37.7 J) is delivered after a confirmation cycle which is also in the VF zone. The slow rhythm is restored with atrial sensing and biventricular pacing.
4 The functioning herein is a textbook case: perfect detection of all the signals, correct diagnosis, quick initiation of the therapy, effective shock, memorization of the episode





