Tachycardia treated by an ATP burst
Patient
A 66-year-old man implanted with Platinium DR for dilated ischemic heart disease without prior infarction and ejection fraction of 28%, narrow QRS, in secondary prevention. Follow-up control. Asymptomatic patient.
Programming

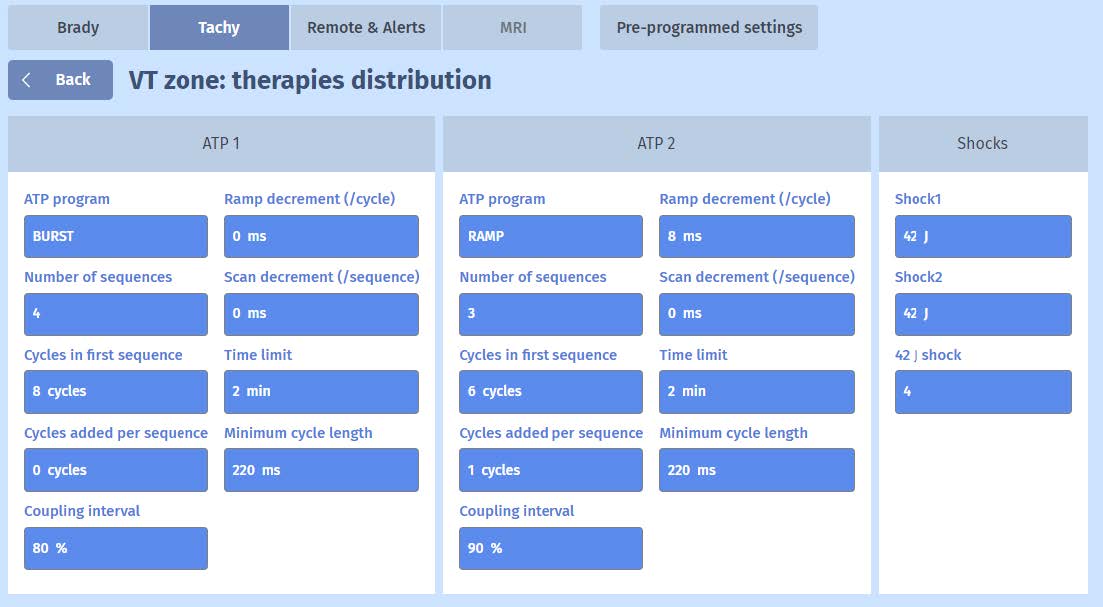
EGM
Explication
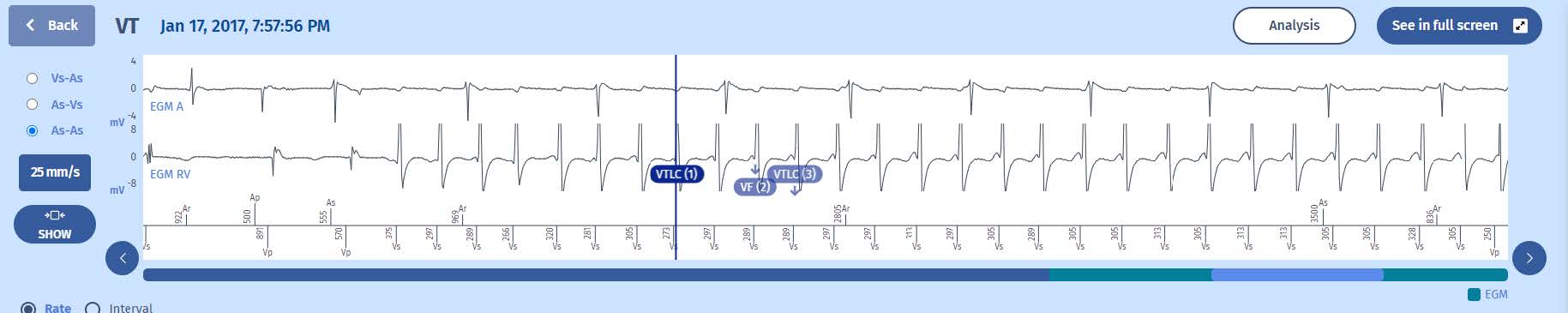
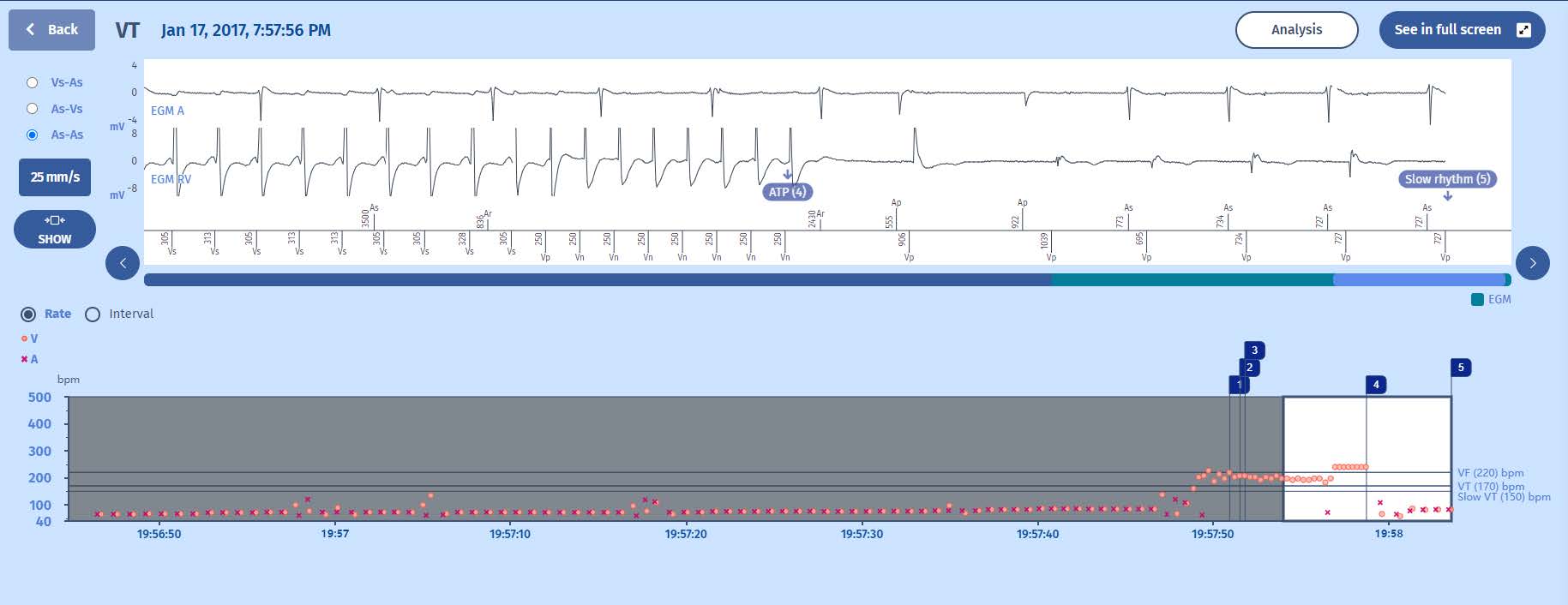
1 The rhythm is sinus and stable.
2 A tachycardia begins, ventricular in nature since the atrial rate remains slow, with some cycles in the VF zone, although the rhythm is predominantly VT with a first VTLC marker, and therefore, a persistence of 20 cycles is started.
3 Then, after 3 cycles, the rhythm becomes predominantly VF, hence a VF persistence is started while the VT counter continues to be incremented by the VF marker.
4 However an additional cycle triggers a return to VT majority (second VTLC marker), and remains as such throughout the persistence of 20 cycles
5 The average of the last 4 persistence cycles is in the VT zone, and it is the first therapy in this zone that is called upon: a burst whose coupling interval is 80% of that of the tachycardia. The ATP cycles are all identical. Not all sinus waves are detected since
falling in the post-ventricular atrial blankings.
Comments
A few operating rules of the MicroPort algorithms:
1 The first two tachycardia cycles in the VT zone are excluded in the initial counting of events.
2 The majority rhythm of the initial 6/8 cycles determines the diagnosis of tachycardia and the number of triggered persistence cycles.
3 VF majority cycles (and the majority they generate) increment the persistence counter of the lower zones
4 The average rate of the last 4 persistence cycles determines the type of therapy that will be initiated based on the zone in which the ventricular tachycardia is located.
The first triggered therapy is the first therapy programmed for the designated zone of the tachycardia, or that previously determined by the Autoswitch ATP function.
Take home message
The triggered therapy is dependent on the average rate of the last 4 persistence cycles that defines the zone in which the arrhythmia is classified, primarily for the VT and Slow VT zones, and in conjunction with other criteria for the FVT zone.



