- this trace shows the value of coupling discriminators for the diagnosis of complex tachycardias such as dual tachycardias; discrimination is performed in stages
- stage 1, V>A : False
- stage 2, at least 3 ventricular cycles out of 10 correlated: false (RID-)
- the analysis continues (step 3) with an analysis of stability and a search for AF
- the AF rate threshold analysis looks for the presence of a fast atrial rhythm, by comparing the various atrial intervals against a programmed threshold (A Fib rate threshold); the atrial analysis begins when ventricular tachyarrhythmia detection is initialized; each atrial interval is classified as either faster or slower than the A Fib rate threshold; when at least 6 of the last 10 intervals are considered to be faster than the A Fib rate threshold, the device declares that AF is present; this parameter can only be programmed in conjunction with stability
- stability analysis is performed by measuring the degree of variability in RR intervals during tachycardia; the differences between ventricular cycles, as well as an average difference, are calculated throughout the Duration; when the Duration expires, rhythm stability is assessed by comparing the current average difference with the programmed Stability and “Shock if unstable” thresholds; if the average difference is greater than the programmed thresholds, the rhythm is declared unstable; independent thresholds are available for the Stability (inhibitory) and “ Shock if unstable” functions
- the idea behind linking the stability and AFib rate threshold criteria is to treat stable rhythms and unstable rhythms without AF (atrial rate < AFib rate threshold), but to inhibit in the presence of an unstable rhythm with atrial rate > AFib frequency threshold (suspicion of conducted AF).
- in this example, the device finds a diagnosis of AF with a stable rhythm (diagnosis of dual tachycardia) and therapies are delivered
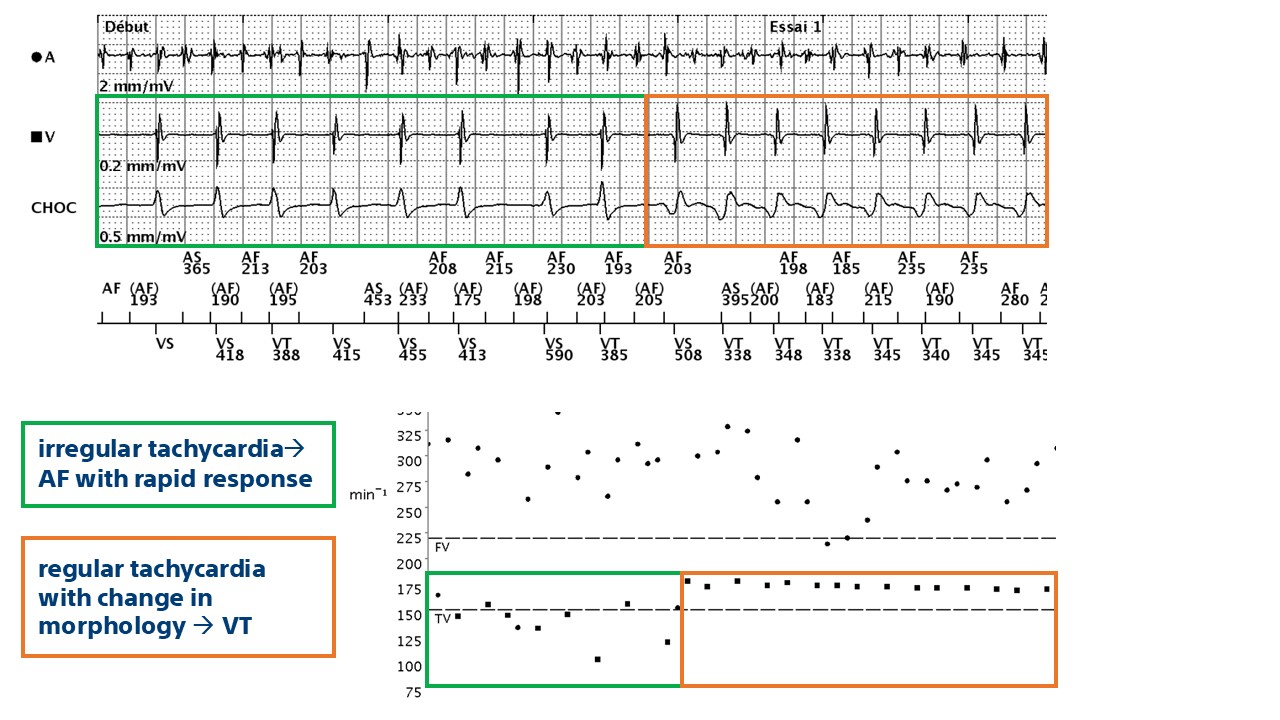
This tracing shows a characteristic appearance of dual tachycardia (AF + VT): atrial activity is rapid and polymorphic (cycles correctly classified as AF); the ventricular channel shows abrupt acceleration with a regular, monomorphic tachycardia with a clear change in signal morphology on the shock channel (VT); the device diagnoses double tachycardia (V>A: False, RID-, AF, stable rhythm) and delivers therapies.